The "Manage VSAN with RVC" series explains how to use Ruby vSphere Console command line to control your VSAN environment. The first part explains basic configuration tasks that are required for the initial setup:
- vsan.enable_vsan_on_cluster
- vsan.disable_vsan_on_cluster
- vsan.apply_license_to_cluster
- vsan.host_consume_disks
- vsan.cluster_set_default_policy
- vsan.host_wipe_vsan_disks
To make commands look better I created marks for a Cluster, a Virtual Machine and an ESXi Hosts. This allows me to use ~cluster, ~vm and ~esx in my examples:
/localhost/DC> mark cluster ~/computers/VSAN-Cluster/ /localhost/DC> mark vm ~/vms/vma.virten.lab /localhost/DC> mark esx ~/computers/VSAN-Cluster/hosts/esx1.virten.lab/
Basic Configuration Tasks
vsan.enable_vsan_on_cluster
Enables VSAN on a cluster. When VSAN is already enabled you can also use this command to enable/disable auto claim. When not specified, auto claim is enabled by default.
Example 1 - Enable VSAN on a Cluster:
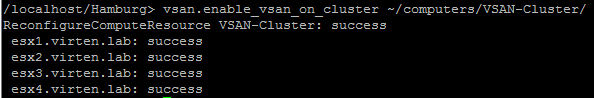
/localhost/DC> vsan.enable_vsan_on_cluster ~cluster ReconfigureComputeResource VSAN-Cluster: success esx1.virten.lab: success esx2.virten.lab: success esx3.virten.lab: success
Example 2 - Disable auto claim on a VSAN enabled Cluster:
/localhost/DC> vsan.enable_vsan_on_cluster --disable-storage-auto-claim ~cluster ReconfigureComputeResource VSAN-Cluster: success esx1.virten.lab: success esx2.virten.lab: success esx3.virten.lab: success
vsan.disable_vsan_on_cluster
Disables VSAN on a cluster. HA has to be disabled to use this command.
Example 1 - Disable VSAN on a HA enabled Cluster:
/localhost/DC> cluster.configure_ha --disabled ~cluster ReconfigureComputeResource VSAN-Cluster: success esx1.virten.lab: success esx2.virten.lab: success esx3.virten.lab: success /localhost/DC> vsan.disable_vsan_on_cluster ~cluster ReconfigureComputeResource VSAN-Cluster: success esx1.virten.lab: success esx2.virten.lab: success esx3.virten.lab: success
vsan.apply_license_to_cluster
Applies a license key to a VSAN Cluster. This command also triggers a Null-Reconfigure of all hosts to ensure that all disks are claimed when auto-claim is enabled.
Example 1 - Apply a VSAN license and for auto-claim:
/localhost/DC> vsan.apply_license_to_cluster -k 00000-00000-00000-00000-00000 ~cluster VSAN-Cluster: Applying VSAN License on the cluster... VSAN-Cluster: Null-Reconfigure to force auto-claim... ReconfigureComputeResource VSAN-Cluster: success esx1.virten.lab: success esx2.virten.lab: success esx3.virten.lab: success
Example 2 - Replace a VSAN license key:
/localhost/DC> vsan.apply_license_to_cluster -r -k 00000-00000-00000-00000-00000 ~cluster VSAN-Cluster: Applying VSAN License on the cluster...
vsan.host_consume_disks
Consumes all eligible disks on a host. When you have multiple SSDs you can specify the appropriate SSD by its model.
Example 1 - Identify SSD Model description and create a disk group. This is required when you have more than one SSD:
/localhost/DC> esxcli.execute ~esx storage core device list [...] IsSSD: true Model: "SanDisk SDSSDP06" [...] /localhost/DC> vsan.host_consume_disks ~esx --filter-ssd-by-model "SanDisk SDSSDP06" AddDisks esx1.virten.lab: success
Example 2 - Add all eligible disks to a new or existing disk group:
/localhost/DC> vsan.host_consume_disks ~esx AddDisks esx1.virten.lab: success
vsan.cluster_set_default_policy
Set default policy on a cluster. That policy is used by default when an object has no VM Storage Policy defined. Available values are:
- hostFailuresToTolerate (Number of failures to tolerate)
- forceProvisioning (Force provisioning)
- stripeWidth (Number of disk stripes per object)
- cacheReservation (Flash read cache reservation)
- proportionalCapacity (Object space reservation)
Default Policy: (("hostFailuresToTolerate" i1) ("forceProvisioning" i1))
Example 1 - Change the default policy to tolerate two host failures:
/localhost/DC> vsan.cluster_set_default_policy ~cluster '(("hostFailuresToTolerate" i2) ("forceProvisioning" i1))'Example 2 - Find out the current default policy from a existing host and add a 3rd Rule:
/localhost/DC> esxcli.execute ~esx vsan policy getdefault
+--------------+----------------------------------------------------------+
| Policy Class | Policy Value |
+--------------+----------------------------------------------------------+
| cluster | (("hostFailuresToTolerate" i1) ("forceProvisioning" i1)) |
| vdisk | (("hostFailuresToTolerate" i1) ("forceProvisioning" i1)) |
| vmnamespace | (("hostFailuresToTolerate" i1) ("forceProvisioning" i1)) |
| vmswap | (("hostFailuresToTolerate" i1) ("forceProvisioning" i1)) |
+--------------+----------------------------------------------------------+
/localhost/DC> vsan.cluster_set_default_policy ~cluster '(("hostFailuresToTolerate" i1) ("forceProvisioning" i1) ("stripeWidth" i2))'vsan.host_wipe_vsan_disks
Deletes the content of all VSAN enabled disks on a host. When the command is uses without the force option it only tells what it would wipe.
Example 1 - Run the command in dry mode:
/localhost/DC> vsan.host_wipe_vsan_disks ~esx Would wipe disk WDC_WD1500HLFS (ATA WDC WD1500HLFS-0, ssd = false) Would wipe disk WDC_WD1500HLFS (ATA WDC WD1500HLFS-0, ssd = false) Would wipe disk WDC_WD1500HLFS (ATA WDC WD1500HLFS-0, ssd = false) Would wipe disk SanDisk_SDSSDP064G (ATA SanDisk SDSSDP06, ssd = true) NO ACTION WAS TAKEN. Use --force to actually wipe. CAUTION: Wiping disks means all user data will be destroyed!
Example 2 - Wipe the content of all VSAN disks:
/localhost/DC> vsan.host_wipe_vsan_disks ~esx --force RemoveDiskMapping esx1.virten.lab: success
Manage VSAN with RVC Series
- Manage VSAN with RVC Part 1 – Basic Configuration Tasks
- Manage VSAN with RVC Part 2 – VSAN Cluster Administration
- Manage VSAN with RVC Part 3 – Object Management
- Manage VSAN with RVC Part 4 – Troubleshooting
- Manage VSAN with RVC Part 5 – Observer
Pingback: Newsletter: December 28 | Notes from MWhite
Pingback: Newsletter: January 12, 2014 | Notes from MWhite
Pingback: Welcome to vSphere-land! » VSAN Links
Pingback: VSAN Configuration Maximum Query Script | virtuallyGhetto
Pingback: vSphere 6 Lab Upgrade – VSAN – DefinIT