In vSphere 7.0, the Windows-based vCenter Server is finally gone. Time to move forward and get in touch with the Linux based Photon OS. The following tips and tricks might come handy when working with the vCenter Server Appliance 7.0:
- Enable SSH
- File Transfer with SCP/SFTP
- Public Key Authentication
- Disable or Increase Shell Session Timeout
- Password expiration
- Reset vCenter Server Appliance 6.7 root password
- Create a Backup Job
- Remove Certificate Warnings (Root CA)
- Install Additional Software
- VMware Datacenter CLI (DCLI)
- Run Docker Containers
Enable SSH
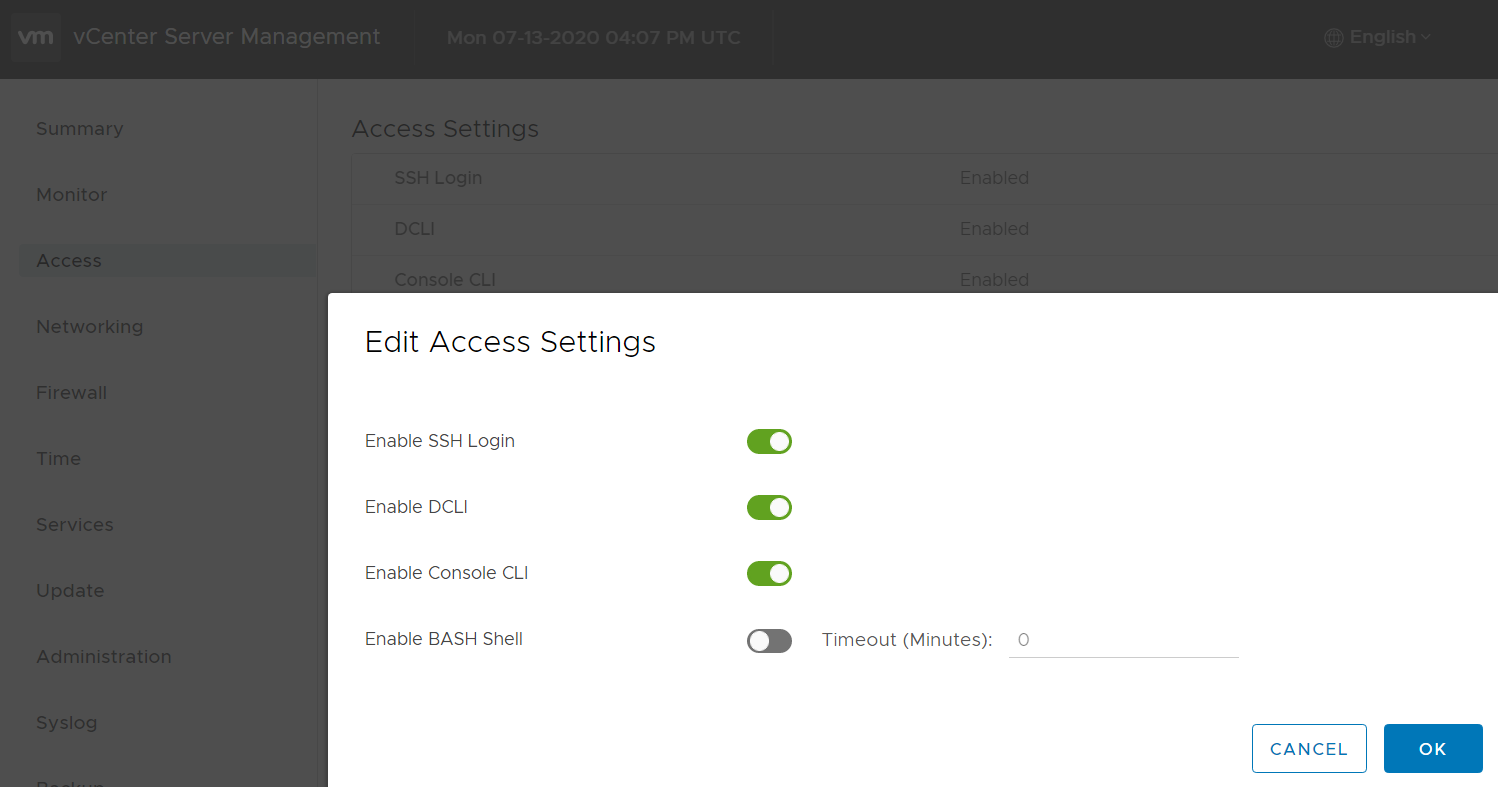
For troubleshooting vCenter and ESXi hosts, SSH is essential. SSH access to the vCenter Server Appliance is disabled by default but can be activated during the deployment wizard. When the vCenter is already deployed you can enable SSH in the "Appliance Management".
Appliance Management (https://[VCENTER]:5480/) > Access > Edit > Enable SSH Login
After connecting to the vCenter with SSH you see the proprietary Appliance Shell. To open the fully-featured Bash, just type "shell".
File Transfer with SCP/SFTP
To transfer files between your PC and the vCenter Appliance you typically use WinSCP or similar tools. This does not work out of the box because the default shell for the root user has been configured to Appliance Shell instead of Bash. When you use WinSCP to connect to the vCSA, the following error is displayed:
Received too large SFTP packet. Max supported packet site is 1024000 B.
Cannot initialize SFTP Protocol. Is this host running an SFTP Server?
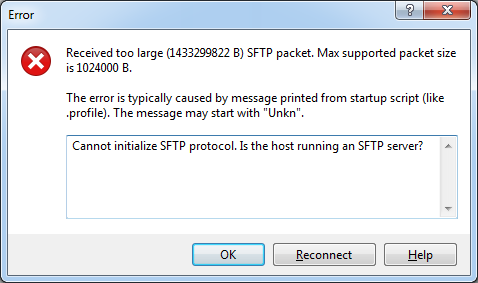
To be able to connect with WinSCP, the default shell has to be configured to /bin/bash:
# chsh -s "/bin/bash" root
If you want to revert this change later and reactivate the Appliance Shell, change the default shell back to /bin/appliancesh:
# chsh -s /bin/appliancesh root
Public Key Authentication
When working with Linux you typically use SSH keys instead of passwords to log in. Public Key authentication is an authentication method that relies on a generated public/private key pair and enables the login without entering a password. If you are not familiar with SSH Public Key Authentication, read this post where I am explaining the basics.
The vCenter Appliance already has a preconfigured authorized_keys file. Just add your key to the file by editing it with vi, or with echo/pipe:
# echo "ssh-rsa AAAAB[....] fgrehl" >> /root/.ssh/authorized_keys
Now you should be able to connect to the vCenter Appliance with your key. Please note that you can't use the Appliance Shell when you log in using an ssh key, so make sure to change the shell to bash:
# chsh -s "/bin/bash" root
Disable or Increase Shell Session Timeout
As a security feature, you are automatically logged out after being inactive for 15 minutes. You can view the current configuration with echo $TMOUT. The value is in seconds (900 seconds = 15 minutes):
# echo $TMOUT 900
The variable has been configured to be readonly, so you can't change it while you are logged in:
# echo $TMOUT 900 # TMOUT=1000 bash: TMOUT: readonly variable
To change the timeout, modify the profile configuration in /etc/profile.d/tmout.sh:
- Open /etc/profile.d/tmout.sh with an editor
- change the line TMOUT=900 to the desired value
- Save and close the file
- Log out and log back in
If you want to completely disable session timeout, delete the tmout.sh script:
# rm /etc/profile.d/tmout.sh
Password expiration
There are two authentication sources where passwords are configured to expire by default. The root user configured in the Appliance Management and all SSO users expire after 90 days. This behavior can be configured:
Root password:
Appliance Management (https://[VCENTER]:5480/) > Administration > Password expiration settings
SSO Users (eg. administrator@vsphere.local):
vSphere Client > Administration > Single Sign-On > Configuration > Local Accounts
Change the Maximum lifetime value
Reset vCenter Server Appliance 7.0 root password
The following method provides steps to recover the vCenter Server Appliance (vCSA) root password. The process is identical in vCenter 6.5, 6.7, and 7.0. The method is officially supported by VMware and documented in KB2147144.
- Take a snapshot of the vCSA to be able to roll back in case of any problems during password recovery.
- Connect to the ESXi Host that runs the vCSA and open a remote console.
- Reboot the vCSA
- Press e immediately after the system starts (When the Photon screen shows up)

- Append rw init=/bin/bash to the line starting with linux
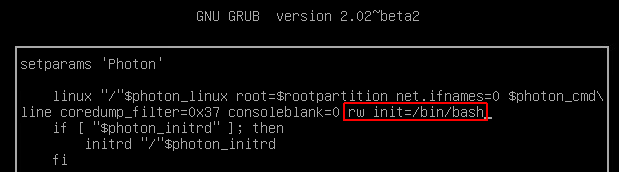
- Press F10 to boot
- In the command prompt, enter passwd and enter a new root password twice
- Enter umount / to unmount the root filesystem
- Reboot the vCSA by running the command reboot -f
- Verify that you can log in with the new root password and delete the snapshot created in step 1.
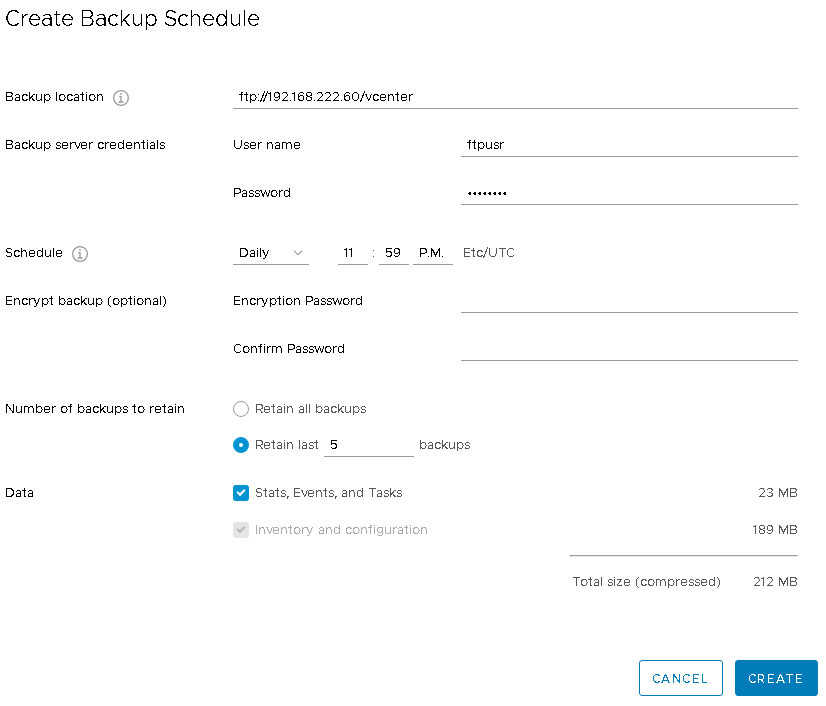
Create a Backup Job
Don't forget to backup your vCenter Server Appliance. The Appliance has an embedded backup scheduler that allows you to create backups without 3rd party tools:
Open Appliance Management (https://[VCENTER]:5480/) and navigate to Backup > Configure
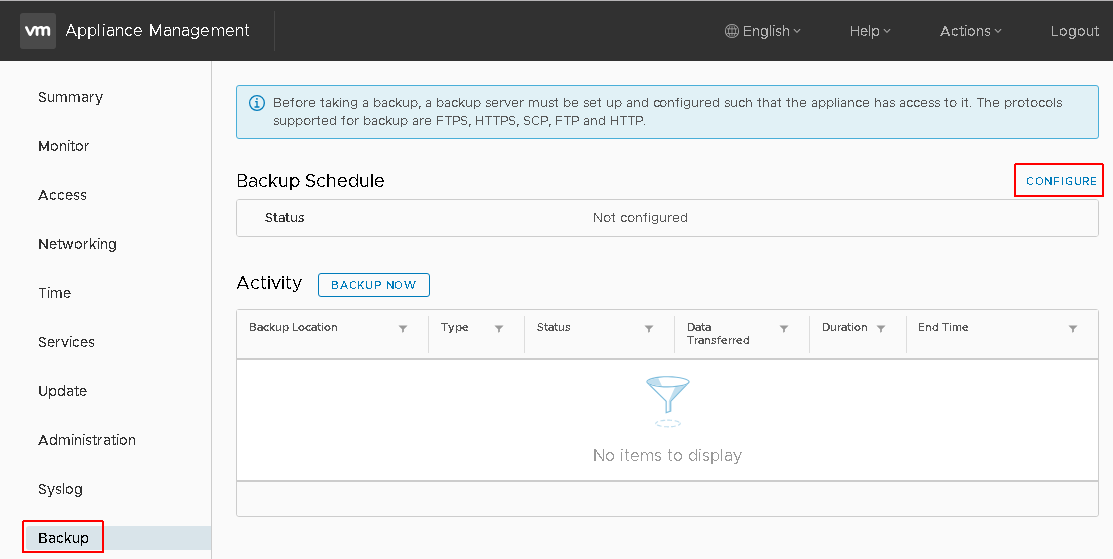 Configure a backup target (FTP, FTPS, HTTP, HTTP or SCP), the backup schedule and a retention policy.
Configure a backup target (FTP, FTPS, HTTP, HTTP or SCP), the backup schedule and a retention policy.
Certificate Warning
To get rid of browser security certificate warnings you have to add the VMCA Root certificate to your local Trusted Root Certificate store. You can download the certificate from the vCenter Website:
- Right-Click "Download trusted root CA certificates" > Save link as...
- Unzip download.zip
- Open the included \certs\win\ directory
- Double-click the .crt file
- Select Install Certificate... > Current User > Place all certificates in the following store > Browse > Trusted Root Certification Authorities
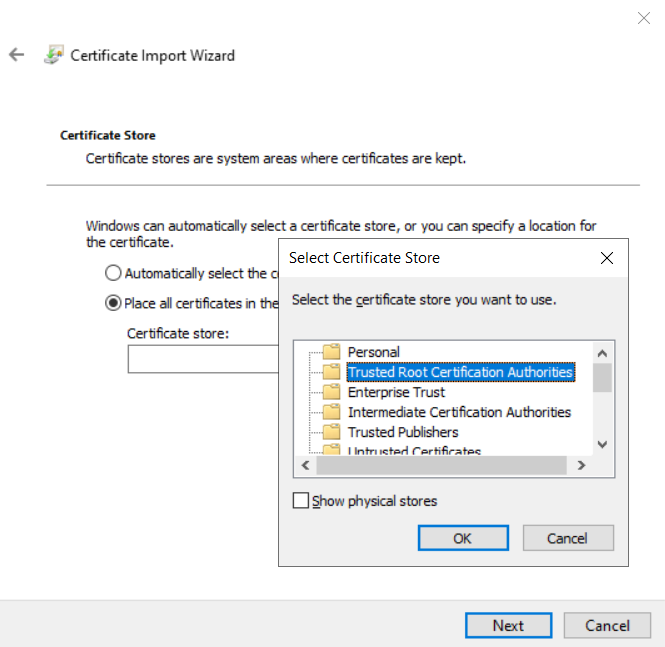
- Finish the wizard
Install Additional Software (eg. PowerShell)
You can install additional software on the vCenter Appliance. Be careful as it might result in an unsupported stat when you install additional software without been advised by VMware GSS. Install additional software with the tdnf package manager. Use tdnf list to list available packages or tdnf search [package] to search for specific packages. You can install PowerShell for example:
# tdnf search powershell powershell : PowerShell is an automation and configuration management platform. # tdnf install powershell -y Installing: userspace-rcu x86_64 0.10.1-1.ph3 photon 638.89k 654221 zlib-devel x86_64 1.2.11-1.ph3 photon 274.67k 281264 lttng-ust x86_64 2.10.2-2.ph3 photon 1.11M 1161968 icu x86_64 61.1-1.ph3 photon 31.02M 32523835 powershell x86_64 7.0.0-1.ph3 photon-updates 118.37M 124118764 Total installed size: 151.39M 158740052 Downloading: userspace-rcu 181074 100% zlib-devel 107545 100% lttng-ust 377915 100% icu 12956251 100% powershell 45304533 100% Testing transaction Running transaction Installing/Updating: icu-61.1-1.ph3.x86_64 Installing/Updating: zlib-devel-1.2.11-1.ph3.x86_64 Installing/Updating: userspace-rcu-0.10.1-1.ph3.x86_64 Installing/Updating: lttng-ust-2.10.2-2.ph3.x86_64 Installing/Updating: powershell-7.0.0-1.ph3.x86_64 Complete! root@vcenter [ ~ ]# pwsh PowerShell 7.0.0 Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. https://aka.ms/powershell Type 'help' to get help. PS /root>
VMware Datacenter CLI (DCLI)
VMware's Datacenter Command-Line Interface (DCLI) is a powerful but widely unknown feature. DCLI uses the vSphere REST API to provide an interactive and scriptable mode to monitor and manage all features made available to the REST-API.
Start the interactive mode with dcli +i and start typing to see possible commands:
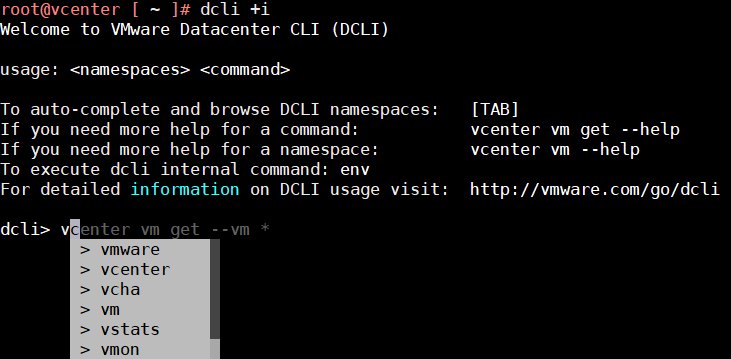
Example:
# dcli +i Welcome to VMware Datacenter CLI (DCLI) usage:To auto-complete and browse DCLI namespaces: [TAB] If you need more help for a command: vcenter vm get --help If you need more help for a namespace: vcenter vm --help To execute dcli internal command: env For detailed information on DCLI usage visit: http://vmware.com/go/dcli dcli> appliance system version get summary: Patch for VMware vCenter Server 7.0.0 install_time: 2020-04-02T12:29:10.005Z product: VMware vCenter Server Appliance build: 16386292 releasedate: June 23, 2020 type: vCenter Server with an embedded Platform Services Controller version: 7.0.0.10400 dcli> com vmware vcenter vm list |---------------|-------|------------------|-----------|---------| |memory_size_MiB|vm |name |power_state|cpu_count| |---------------|-------|------------------|-----------|---------| |512 |vm-1001|vy |POWERED_ON |1 | |12288 |vm-1003|vcenter.virten.lab|POWERED_ON |2 | |16384 |vm-1016|nsx1.virten.lab |POWERED_ON |4 | |---------------|-------|------------------|-----------|---------| dcli>
If you already the resource to pull you can run dcli in scripted mode:
# dcli com vmware vcenter vm list |---------------|-------|------------------|-----------|---------| |memory_size_MiB|vm |name |power_state|cpu_count| |---------------|-------|------------------|-----------|---------| |512 |vm-1001|vy |POWERED_ON |1 | |12288 |vm-1003|vcenter.virten.lab|POWERED_ON |2 | |16384 |vm-1016|nsx1.virten.lab |POWERED_ON |4 | |---------------|-------|------------------|-----------|---------|
Run Docker Containers
You can run Docker containers on the vCenter Appliance. See Docker Hub for available Container Images.
- Install Docker
# tdnf -y install docker
- Start Docker and load Kernel Bridge Modules
# systemctl enable docker # insmod /usr/lib/modules/$(uname -r)/kernel/net/bridge/bridge.ko.xz # systemctl start docker
If you get an error, try replacing "bridge.ko.xz" with "bridge.ko".
- Pull a Docker Image
# docker pull vmware/powerclicore
- Start a Docker Container
# docker run --rm -it vmware/powerclicore
Trying to disable the root password expiration on vcs 7, following your instructions in the appliance, there's no "Administration" section to navigate to.
Das Problem hatte ich auch.
Anmeldung als "administrator" sieht keine Administration, aber Anmeldung als "root" geht.
I don't understand, English please...
Logging in as "administrator" does not see administration, but logging in as "root" works.